Why Assessment & Diagnostics Matter in Diabetic Foot
Intrroduction
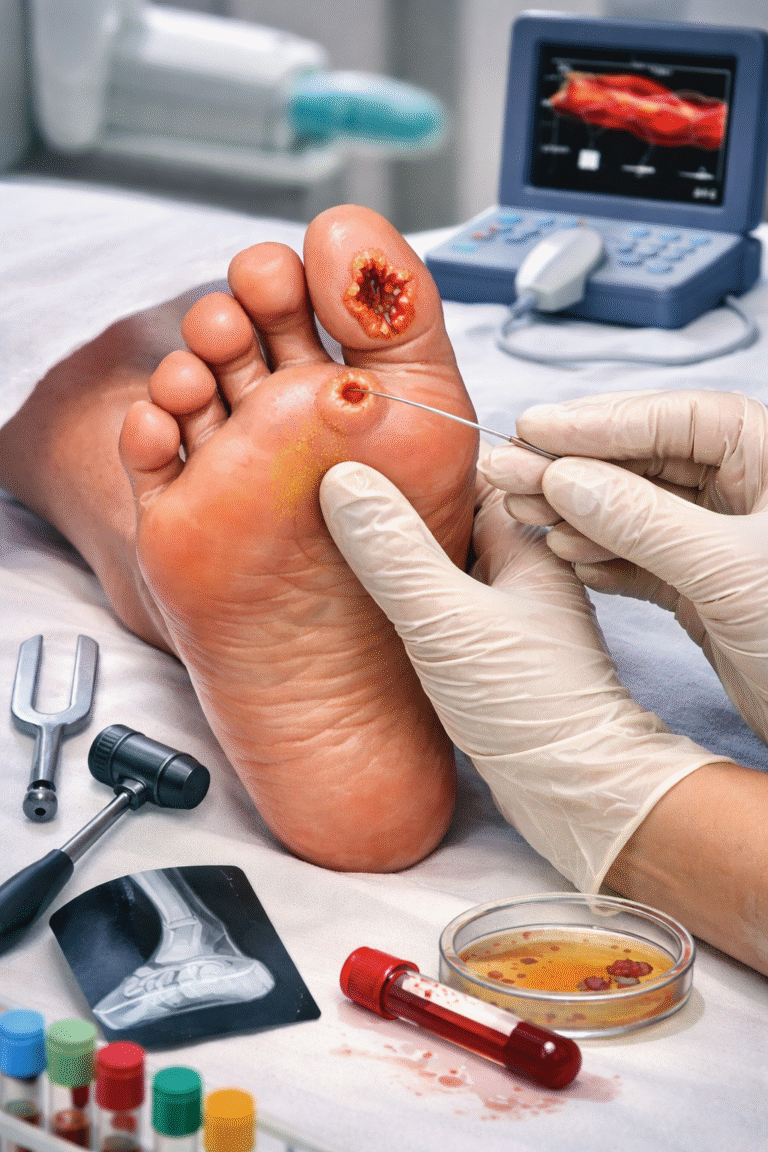
Diabetic patients are at high risk for foot ulcers, infections, neuropathy, vascular disease, and amputations due to poor blood supply and nerve damage. There is loss of sensation in diabetics causing diabetic neuropathy. Earl and accurate assessment is the most important step in preventing complications.
A comprehensive Diabetic Foot Assessment identifies
- Nerve damage
- Poor blood circulation
- High-pressure points
- Foot deformities
- Deep infections
- Bone involvement
- Severity of the wound
At Happy Diabetic Foot & Podiatry Centre, we follow advanced diagnostic protocols to ensure timely treatment, faster healing, and prevention of future ulcers.
Neurological Assessment in Diabetic Foot
In this we detect loss of protective sensation caused by diabetic neuropathy.
We check
- Peripheral nerve function
- Sensation and reflexes
- Motor function & muscle weakness
Diabetic Neuropathy Assessment Tests done are
- 10g Monofilament test – to assess light touch
- Vibration test (128 Hz tuning fork) – to detect vibration sense loss
- Pinprick sensation
- Temperature discrimination
- Ankle reflexes
The loss of protective sensation increases the risk of
- Painless ulcers
- Blisters
- Charcot foot
- Repeated injuries
Vascular Assessment for diabetic foot
It is done to evaluate blood circulation to the foot and identify PAD (Peripheral Artery Disease).
a) ABI test – Ankle Brachial Index
ABI compares blood pressure in the ankle vs. arm to indicate blockage.
Normal ABI: 0.9 – 1.3
Low ABI (<0.9): Suggests PAD
High ABI (>1.3): Calcified arteries – need Doppler evaluation
b) Doppler Ultrasound
It is done to check for
- Blood flow
- Arterial blockage
- Venous insufficiency
- Quality of circulation
If there is poor blood supply, it can lead to
- Non-healing ulcers
- Gangrene
- Risk of amputation
Foot Pressure Assessment
It is done to identify areas of high pressure that can cause ulcers.
Foot pressure test in diabetics measures
- Foot pressure distribution
- Weight-bearing abnormalities
- Risk zones for ulcer formation
- Effects of deformities (hammer toe, claw toe, flat foot, bunions)
The high pressure in foot can lead to
- Calluses
- Corns
- Ulcers
- Recurrent wounds
Foot or plantar press analysis guides the creation of custom diabetic footwear, insoles, and offloading devices.
Foot Scan & Gait Analysis
The purpose is to evaluate foot shape, arch, alignment, and walking pattern.
This test helps to assess
- 3D foot structure
- Arch height & pronation
- Toe deformities
- Joint abnormalities
- Gait cycle (heel strike, toe-off)
Blood Sugar Evaluation
Tests done are
- Fasting blood sugar
- Post-prandial blood sugar
- HbA1c (3-month control)
- Random sugar during visit
Uncontrolled sugars can leads to
- Slow wound healing or foot ulcers
- High infection risk
- Neuropathy progression
- Increased chances of hospitalization
Diabetes should be under control for faster wound healing.
Infection Work-Up
It is essential to detect soft-tissue and deep infections.
The tests done are
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- ESR & CRP – inflammation markers
- Wound swab culture & sensitivity
- Pus culture
- Blood culture is done if there is severe infection
It guides in
- Antibiotic selection according to pus or wound culture
- Surgical management like debridement or amputation
X-Ray & MRI for Bone Involvement
X-Ray detects
- Bone erosion
- Gas in tissues
- Foreign bodies
- Charcot foot changes
- Fractures
MRI is the Gold standard for
- Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
- Deep abscess
- Soft-tissue involvement
- Early Charcot foot
Wound Grading Systems (Wagner Classification)
This grading system helps to decide treatment and predict healing.
Wagner Classification
Grades 0–5 based on ulcer depth & gangrene.
0 – No ulcer, high risk foot
1 – Superficial ulcer
2 – Deep ulcer, tendon/bone exposed
3 – Abscess, osteomyelitis
4 – Localized gangrene
5 – Full foot gangrene
