Infection & Gangrene in Diabetics – Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Introduction
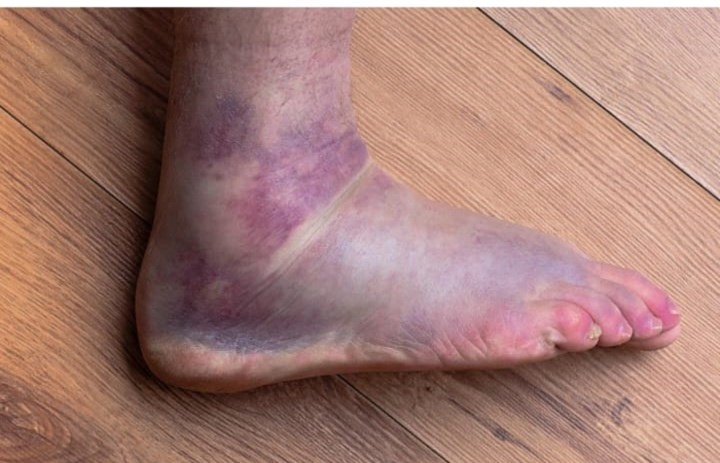
Diabetic patients are at a significantly higher risk of foot infections and gangrene due to poor blood circulation, nerve damage, weakened immunity, and delayed wound healing. Even a small cut, blister, or scratch can progress into a serious infection, leading to ulcers, abscesses, bone infection (osteomyelitis), sepsis, or gangrene.
Blood supply to a part of the foot is completely lost, causing tissue death, this leads to gangrene and it is a surgical emergency.
At our Diabetic Foot & Podiatry Center, we provide early diagnosis, infection control, and advanced limb-salvage treatments for diabetic foot infections and gangrene.
Causes of Infection & Gangrene in Diabetics
1. Neuropathy (Loss of Sensation)
Patients may not feel cuts, blisters, sharp objects and burns. These unnoticed injuries get infected easily.
2.Poor Blood Circulation (Peripheral Artery Disease)
Decreased blood flow causes slow healing, increased infection risk, and high gangrene risk
3.High Blood Sugar Levels
High glucose weakens the immune system and feeds bacteria, worsening infection.
4.Foot Deformities
Hammer toe, claw toe, bunions cause pressure points leading to ulcers which in turn causes infection.
5.Poor Foot Care
Walking barefoot, cracked heels, untrimmed nails, footwear injuries.
6.Delayed Treatment
Small wounds can progress to Cellulitis, abscess, bone infection and tissue death
Symptoms of Infection in Diabetic Foot
- Redness and swelling
- Warmth or hot skin
- Pus discharge
- Foul smell
- Increased pain (if sensation is present)
- Blackened areas on skin
- Fever or fatigue
- Spreading redness up the leg
Symptoms of Gangrene
- Black, blue, or brown discoloration
- Cold and numb toes/foot
- Severe foul-smelling discharge
- Dry, shriveled skin (dry gangrene)
- Wet, swollen, soft tissues (wet gangrene)
- Gas bubbles under skin (gas gangrene)
- Severe weakness or high fever
Gangrene is an surgical emergency and needs immediate intervention.
Diagnosis of Infection & Gangrene
1.Physical Examination
- Ulcer assessment
- Depth of wound
- Presence of pus
- Colour changes
- Odour
2.Blood Tests
CBC, CRP, ESR, Blood sugar levels And Kidney tests
3.Wound Cultures is done to identify bacteria and choose the correct antibiotics.
4.Doppler Study to check blood supply to the foot.
5.X-Ray of the Foot
Detects bone infection (osteomyelitis), gas in tissues.
6.MRI Scan to look for deep infections and abscesses.
7.Angiography is done to assess arterial blockages if gangrene is suspected.
Treatment of Infection & Gangrene
Treatment depends on severity and extent of tissue damage.
- Blood Sugar should be in control because it will fasten the healing process and stops the infection progression.
- Antibiotics should be selected based on culture report. Oral antibiotics for mild infections and IV antibiotics for moderate to severe cases.
- Wound Debridement is done to remove dead tissue, pus, slough and infected material. Wound debridement helps in wound healing and prevents the spread
4.Advanced Dressings
There are different types of dressings which can be done in diabetic foot
- Hydrocolloid dressings
- Foam dressings
- Antimicrobial dressings
- VAC therapy for deep or chronic wounds
- Infection Drainage
Abscesses or deep infections may require surgical drainage.
- Revascularization (To Improve Blood Flow)
In gangrene or severe infection there is poor blood supply. Angioplasty, Stenting or Bypass surgery will restore circulation and prevents amputation.
- Surgical Treatment
In surgical treatment there are 3 options depending on patients condition
- Removal of dead tissue
- Minor amputations (toes, part of foot)
- Major amputation (last resort only)
Goal: save maximum limb and life.
- Offloading & Specialized Footwear prevents pressure on wounds and reduces re-injury.
Blisters & Skin Changes in Diabetics – Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Introduction
The skin changes like blisters, cracks, calluses, dry skin, fungal infections, and color changes occurs in diabetics due to nerve damage, poor circulation, and impaired immunity. These skin problems have to be identified early and treated, otherwise it can lead to ulcers and infections.
Causes of Blisters & Skin Changes in Diabetics
- Peripheral Neuropathy
Due to peripheral neuropathy there is loss of sensation in legs and feet which can cause repetitive unnoticed trauma leading to blisters.
- Poor Circulation
Skin becomes thin, fragile, dry and hence easily damaged.
- High Blood Sugar
High sugars can cause dry, cracked skin, increased risk of fungal infections and slower healing
- Ill-Fitting Footwear
If the footwear are not fitting properly then it increases the pressure and friction on feet and cause calluses, corns and blisters.
- Reduced Sweat Production
In diabetic patients autonomic neuropathy reduces sweating leading to dry and cracked skin.
- Foot Deformities
The foot deformities like claw toe or hammer toe increases pressure points which leads to hard skin and blisters in the foot.
Symptoms of Skin Changes in Diabetics
Common Signs
- Clear fluid-filled blisters
- Peeling or cracked skin
- Thick calluses or corns
- Dry or scaly skin
- Discoloration (red, brown, pale patches)
- Fungal infections between toes
- Itching or burning sensation
Warning Signs
- Wet blisters with pus
- Skin turning blue, black, or cold
- Open wounds
- Foul smell
These could indicate infection.
Diagnosis of Blisters & Skin Changes
- Clinical Examination
The patient has to be
Assessed for blister depth, skin dryness, callus thickness and foot structure
- Blood Sugar Evaluation
If the blood sugars are high then it can lead to recurrent skin problems.
- Infection Screening
Pus/wound culture has to be sent to look for the organism and start the antibiotics which is susceptible
- Vascular Assessment
If the doctor suspects poor circulation then he can advise Doppler or ABI.
- Foot Pressure Scan
This scan is advised to identify friction/pressure points causing blisters.
Treatment of Blisters & Skin Changes
- Do NOT Burst Blisters
It increases the risk of infection.
- Dressing
- Treating Dry Skin
Apply Moisturizing creams which are urea-based creams and avoid harsh soaps.
- Callus & Corn Removal
These should be removed by a podiatrist or diabetic foot specialist, self treatment should be avoided
- Footwear Correction
The footwear should be soft and cushioned, offloading insoles and custom orthotics. This will prevents recurrent skin problems.
- Treating Infections
If there is infection then it should be treated with Antifungals or antibiotics.
- Blood Sugar Control
Strict blood sugar control is advised as it improves skin health and healing.
- Patient Education
Patient is advised to about daily foot inspection, avoid barefoot walking and proper nail care
